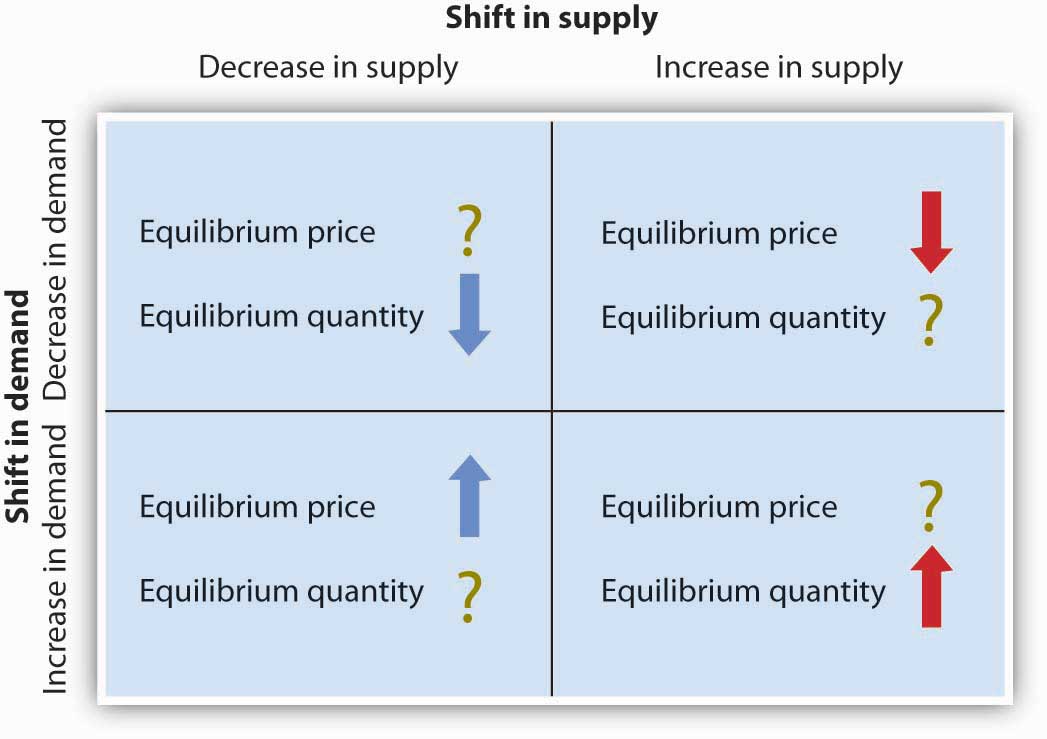
In the following question you are asked to determine other things equal the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product x upon 1 the demand d for or supply s of x.
Decrease in demand price floor change.
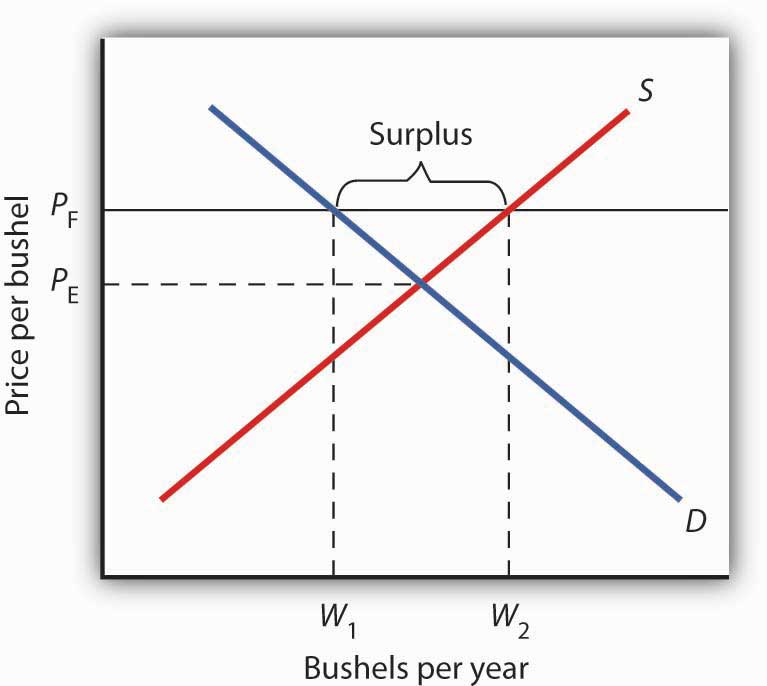
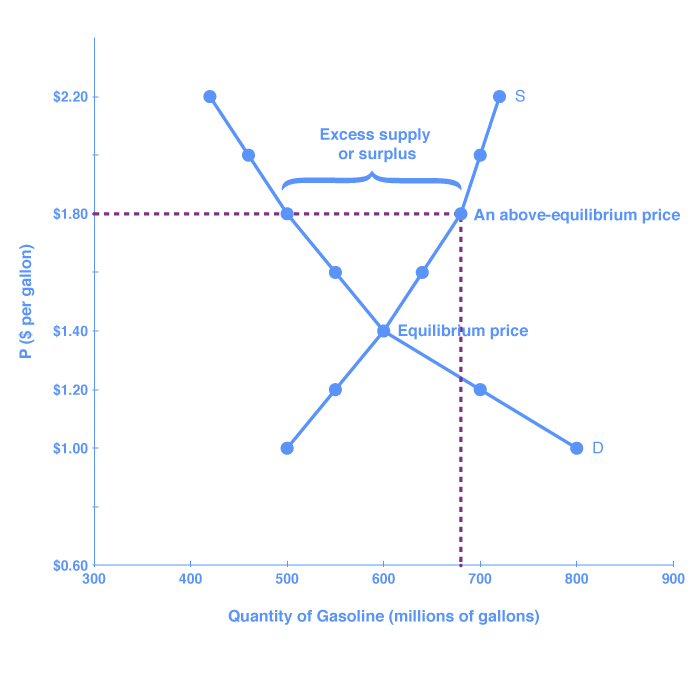
If the price is not permitted to rise the quantity supplied remains at 15 000.
The change means an increase or decrease in the volume of demand and supply from its equilibrium.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
Price ceilings and price floors.
2 the equilibrium price p of x.
Subsidies will increase supply b c part of cost to make will be reimbursed think farmers growing corn taxes will decrease supply b c it is more expensive.
A change in supply.
And very low prices naturally.
Demand curves are used to estimate behaviors in competitive markets and are often used with supply curves to estimate the market equilibrium price or the price at which sellers are willing to sell the same amount of a product as the market s buyers are willing purchase.
1 a change in demand 2.
O other goods change in price demand a decrease in the demand for another good supplied by a firm would cause the firm to shift its resources and increase the supply of remaining goods s subsidies change change in subsidies or taxes.
This is the currently selected item.
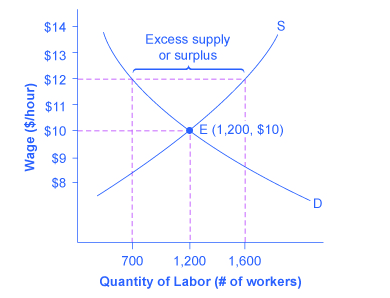
How price controls reallocate surplus.
Minimum wage and price floors.
And 3 the equilibrium quantity q of x.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
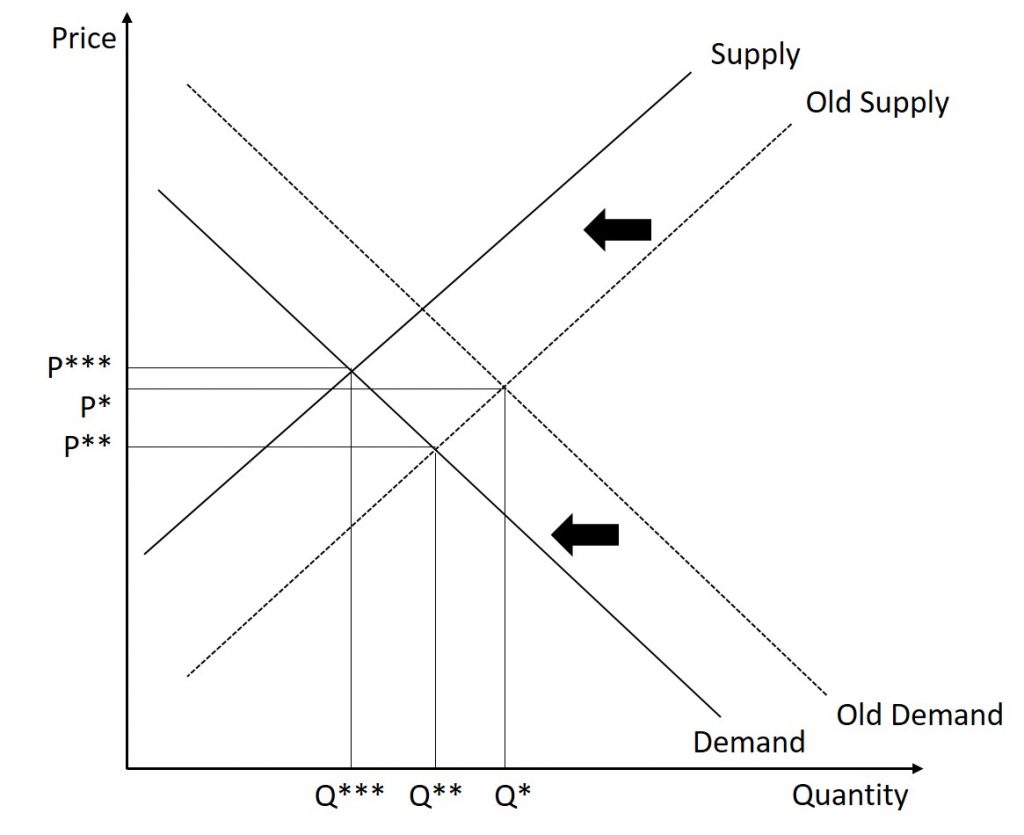
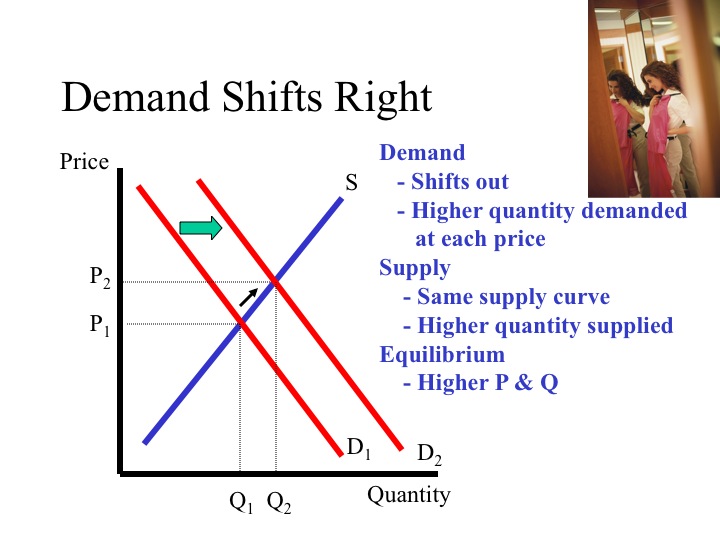
The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e 0 if demand shifts from d 0 to d 1 the new equilibrium would be at e 1 unless a price ceiling prevents the price from rising.
If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy.
At higher market price producers increase their supply.
Taxes and perfectly elastic demand.
Decrease in demand both prices and quantities decrease.
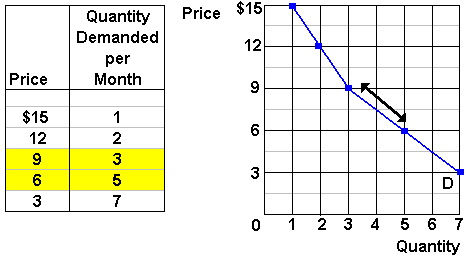
When price increases by 20 and demand decreases by only 1 demand is said to be inelastic.
Key takeaways key points.
Taxation and deadweight loss.
There exist some determinants other than the price of the commodity which affects the quantity of demand like the income of consumers the taste of consumers preference of consumers population technology etc.
A price floor would be established in cases where the government believed the market equilibrium price would.
A price ceiling example rent control.
In contrast consumers demand for the commodity will decrease and supply surplus is generated.
If demand increases demand curve will shift to d 1 d 1 and the new equilibrium price will rise to op 1 and quantity demanded and supplied will increase to oq 1 similarly when demand curve shifts downward to d 2 d 2 price and quantity decline to op 2 and oq 2 respectively.
4 25 b the supply curve has been assumed to be perfectly elastic.
But if price floor is set above market equilibrium price immediate supply surplus can be observed.
Can the laws of demand and supply be repealed.
Governments put in place price floors in markets with inelastic demand inelastic demand inelastic demand is when the buyer s demand does not change as much as the price changes.






/QuantitySupplied2-98c4fd9fe04e4ec78318d9dd87f2c93e.png)